基本概念
官网 https://docs.scipy.org/doc/
numpy的主要对象是同种元素的多维数组。
这是一个所有的元素都是一种类型、通过一个正整数元组索引的元素表格(通常是元素是数字)。
在numpy中维度(dimensions)叫做轴(axis),轴的个数叫做秩(rank)。
- eg:
[1, 2, 3] - eg:
[[ 1. 0. 0.] [ 0. 1. 2.]]
numpy的数组类被称作ndarray。通常被称作数组。注意numpy.array和标准Python库类array.array并不相同,后者只处理一维数组和提供少量功能。更多重要ndarray对象属性有:
ndarray.ndim 数组轴的个数,轴的个数被称作秩
ndarray.shape 数组的维度。这是一个指示数组在每个维度上大小的整数元组。
eg:一个2行3列的矩阵,它的shape属性将是(2,3),这个元组的长度是秩,即维度或者ndim属性ndarray.size 数组元素的总个数,等于shape属性中元组元素的乘积。
ndarray.dtype 一个用来描述数组中元素类型的对象。
ndarray.itemsize 数组中每个元素的字节大小。
eg:import numpy as np arr = np.arange(15).reshape(3, 5) print("arr", arr) print("shape", arr.shape) # (3,5) print("dtype", arr.dtype) # (int32) print("size", arr.size) # 15 print("type", type(arr)) # <class 'nu py.ndarray'>
创建数组
- 使用array函数从常规的Python列表和元组创造数组。
所创建的数组类型由原序列中的元素类型推导而来。import numpy as np arr = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4]) # [1, 2, 3, 4] print(arr) - 可以在创建时显示指定类型
import numpy as np arr = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4],dtype=np.float32) # [1. 2. 3. 4.] print(arr) zeros创建一个全是0的数组
参数:zeros(shape, dtype = float, order = 'C')import numpy as np arr = np.zeros((2,3)) print(arr) #float64 print(arr.dtype)ones创建一个全1的数组
参数:ones(shape, dtype=None, order='C')import numpy as np arr = np.ones((2,3)) print(arr) #float64 print(arr.dtype)empty创建一个内容随机并且依赖与内存状态的数组
参数:empty(shape, dtype = float, order = 'C')import numpy as np arr = np.empty((2,3)) print(arr) #float64 print(arr.dtype)arange函数返回数组
参数:arange(start = None, stop = None, step = None, dtype = None)
由于有限的浮点数精度,通常无法预测获得的元素个数。import numpy as np arr = np.arange(10,40,10) #[10 20 30] print(arr) #int32 print(arr.dtype)linspace返回数组
参数:linspace(start, stop, num=50, endpoint=True, retstep=False, dtype=None)import numpy as np arr = np.linspace(0,9,10) #[0. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9.] print(arr) #float64 print(arr.dtype)
random 类
numpy中利用random类获取随机数.
random()
生成随机浮点数
默认为生成一个随机的浮点数,范围是在0.0~1.0之间,也可以通过参数size设置返回数据的size。
import numpy as np
# 生成一个随机的浮点数
r = np.random.random()
# 0.6590899579137934
print (r)
'''
[[0.89269339 0.56326053 0.79697541]
[0.69644276 0.17902598 0.0084224 ]]
'''
# 指定size
print(np.random.random(size=(2,3)))
randint()
产生随机整数
参数: randint(low, high=None, size=None, dtype=’l’) 如果 high为None(默认值),则结果为[0,low ]
默认随机生一个整数int类型,可以指定这个整数的范围。
import numpy as np
# 产生 0-4 一个
print(np.random.randint(4))
# 产生 2-4 一个
print(np.random.randint(2,4))
# 产生 1-5 两个
print(np.random.randint(low=1,high=5,size=2))
# 产生 0-5 三个
print(np.random.randint(5, size=3))
# 产生 0-10 2行3列(2*3)
print(np.random.randint(10, size=(2, 3)))
normal()
高斯分布
参数: normal(loc=0.0, scale=1.0, size=None) loc:均值,scale:标准差,size:抽取样本的size 。
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
y=np.random.normal(0,1,5000)
print(y)
# 直方图
# 100个分块
plt.hist(y,bins=100)
plt.show()
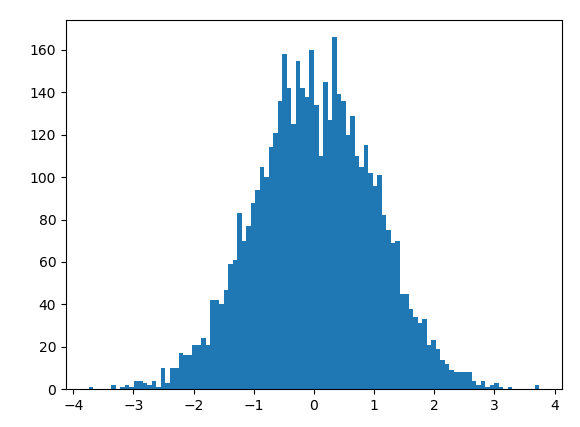
randn()
正态分布产生一个浮点数或N维浮点数组 参数:randn(d0, d1, ..., dn)
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
y=np.random.randn(1000)
# 直方图
# 100个分块
plt.hist(y,bins=100)
plt.show()
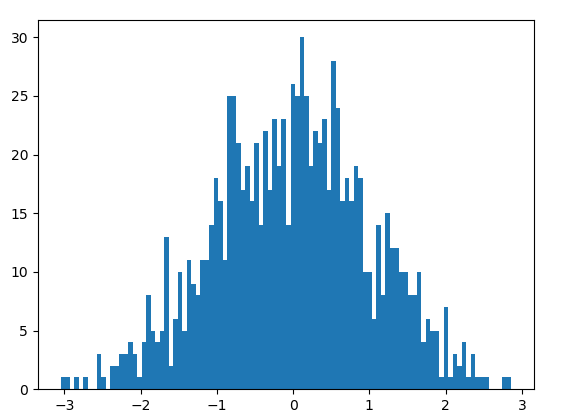
standard_normal
标准正态分布产生一个浮点数或N维浮点数组 参数:standard_normal(size=None)
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
y=np.random.standard_normal((2000,1))
# 直方图
# 100个分块
plt.hist(y,bins=100)
plt.show()
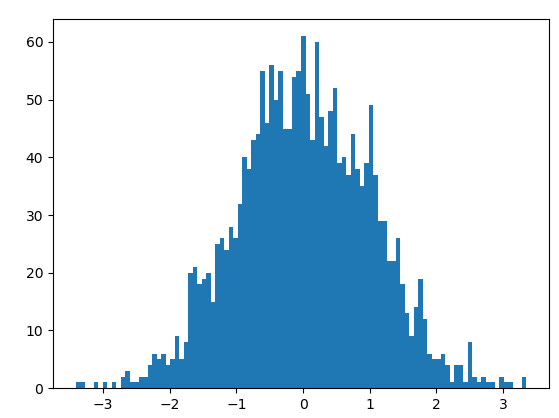
rand()
生成[0, 1) 间随机数
import numpy as np
# 0.7758272442386239
print(np.random.rand())
'''
[[0.07675678 0.72700556 0.31372113]
[0.19674323 0.3332258 0.49691272]]
'''
print(np.random.rand(2,3))
shuffle()
随机打乱序列将序列的所有元素随机排序
import numpy as np
x=np.arange(10)
# [0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9]
print(x)
np.random.shuffle(x)
# 并没有产生新的数组
# [7 6 1 9 3 8 4 2 5 0]
print(x)
choice()
随机选取序列的一个元素,可以从序列(字符串、列表、元组等)中随机选取,返回一个列表,元组或字符串的随机项。
import numpy as np
x=np.arange(10)
# [0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9]
print(x)
# 5
print(np.random.choice(x))
# 输出6个小于5的元素
# [1 3 2 2 1 1]
print(np.random.choice(5, 6))
import numpy as np
# 每个条目出现的概率。如果没有就均匀分布
# [0 3 2]
print(np.random.choice(5, 3, p=[0.1, 0, 0.3, 0.6, 0]))
x = ['a', 'b', 'c', 'd']
# ['a' 'c']
print(np.random.choice(x, 2, p=[0.1, 0, 0.9, 0]))
RandomState()
指定种子值,如不设置种子值时,np.random.randint(10)可能产生0-10内的任意整数,且每次产生的数字可能是任意一种。
设置种子值后,np.random.RandomState(0).randint(10)可能产生0-10内的任意整数,如果种子值不变则每次运行程序产生的数字一样。
import numpy as np
print(np.random.RandomState(0).randint(10))
print(np.random.RandomState(2).randint(10))
print(np.random.randint(10))
基本运算
数组的算术运算是按元素的。新的数组被创建并且被结果填充。
import numpy as np
a = np.array([1, 3, 5, 7, 9])
b = np.array([2, 4, 6, 8, 10])
# +
print(a+b)
# -
print(a-b)
# *
print(a*b)
# /
print(a/b)
# ^ **平方
print(b**2)
# %
print(b % 3)
# 并没有产生新的数组
print('------')
b += 2
print(b)
# -=
b -= 2
print(b)
# *=
b *= 2
print(b)
通用函数(ufunc)
numpy提供常见的数学函数如sin,cos和exp叫作“通用函数”(ufunc)。
这些函数作用按数组的元素运算,产生一个数组作为输出。
import numpy as np
x =np.arange(5)
# [0 1 2 3 4]
print(x)
# [ 0. 0.84147098 0.90929743 0.14112001 -0.7568025 ]
print(np.sin(x))
# [ 1. 0.54030231 -0.41614684 -0.9899925 -0.65364362]
print(np.cos(x))
# [0. 1. 1.41421356 1.73205081 2. ]
print(np.sqrt(x))
# [ 1. 2.71828183 7.3890561 20.08553692 54.59815003]
print(np.exp(x))
索引,切片和迭
索引模式:start:stop:step
- 一维数组可以被索引、切片和迭代,就像列表和其它Python序列。
- 多维数组可以每个轴有一个索引。这些索引由一个逗号分割的元组给出。
- 当少于轴数的索引被提供时,确失的索引被认为是整个切片。
- 迭代多维数组是就第一个轴而言的。
- 对每个数组中元素进行运算,可以使用flat属性,该属性是数组元素的一个迭代器。
import numpy as np
x=np.arange(10)**2
# [ 0 1 4 9 16 25 36 49 64 81]
print(x)
# 1
print(x[1])
# [1 4]
print(x[1:3])
# [1 9]
print(x[1:5:2])#start:stop:step
idx=[1,2,3]
# [1 4 9]
print(x[idx])
for item in x :
print(item)
#--------------
m=np.arange(20).reshape(4,5)**2
'''
[[ 0 1 4 9 16]
[ 25 36 49 64 81]
[100 121 144 169 196]
[225 256 289 324 361]]
'''
print(m)
# 多维索引
# 169
print(m[2,3])
'''
[[ 9]
[ 64]
[169]]
'''
print(m[0:3,3:4])# 0,1,2 行 3列
# [225 256 289 324 361]
print(m[-1])
for item in m.flat:
print(item)
形状操作
- reshape函数改变参数形状并返回它,而resize函数改变数组自身
import numpy as np
x = np.arange(12)
# [ 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11]
print(x)
# (12,)
print(x.shape)
# reshape函数改变参数形状并返回它,而resize函数改变数组自身。
# 返回新的数组
print(x.reshape(3, 4))
x.resize(3, 4)
print(x)
x.shape = (3, 4)
print(x)
# [ 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11]
print(x.ravel())
a = np.array([[1, 2],
[3, 4]])
b = np.array([[5, 6],
[7, 8]])
'''
[[1 2]
[3 4]
[5 6]
[7 8]]
'''
print(np.vstack((a, b)))
'''
[[1 2 5 6]
[3 4 7 8]]
'''
print(np.hstack((a, b)))
布尔数组索引
import numpy as np
x = np.arange(12).reshape(3, 4)
'''
[[ 0 1 2 3]
[ 4 5 6 7]
[ 8 9 10 11]]
'''
print(x)
y = x > 6
'''
[[False False False False]
[False False False True]
[ True True True True]]
'''
print(y)
x[y]=100
'''
[[ 0 1 2 3]
[ 4 5 6 100]
[100 100 100 100]]
'''
print(x)
ref
方法
| numpy方法 | 解释 |
|---|---|
| np.dtype | 指定当前numpy对象的整体数据类型 |
| np.itemsize | 对象中每个元素的大小, 单位字节 |
| np.size | 对象元素的个数, 相当于np.shape中的n*m值 |
| np.shape | 轴, 查看数组形状, 对于矩阵, n行m列 |
| np.ndim | 秩 |
| np.isnan(list) | 筛选出nan值 |
| np.iscomplex(list) | 筛选出非复数 |
| ~ | 取补运算符 |
| np.array(数组, dtype=np.bool) | 自定义数组类型 |
| np.astype(np.bool) | 转换数组类型 |
| np.mat() | 将python 列表转化成矩阵 |
| np.mat().getA() | 将matrix对象转成ndarray对象 |
| np.matrix() | 同上 |
| np.asmatrix() | 将ndarray对象转成matrix对象 |
| np.tile() | 重复某个数组。比如tile(A,n),功能是将数组A重复n次,构成一个新的数组 |
| np.I | 矩阵求逆 |
| np.T | 矩阵转置, 行变列, 列变行, 对角线翻转矩阵 |
| np.tolist() | 转换成python列表, 用于和python原生结合写程序 |
| np.multiply(x, y) | 矩阵x 矩阵y相乘 |
| np.unique() | 数组驱虫, 并且从小到大生成一个新的数组 |
| np.arange | 同python range() |
| np.arange(24).reshape((2, 3, 4)) | 创建一个2维3行4列的数组, 必须能被给定的长度除开, 可以索引和切片 |
| np.arange(24).resize((2, 3, 4)) | 同上, 会修改原值 |
| np.linspace(x, y, z) | 等间距生成, x起始, y截止, z步长 |
| np.ones(x) | 生成都是x的数组, 可传递三维数组, 几行几列, 具体的个数 |
| np.zeros(x) | 生成都是0的数组 |
| np.full([x, y], z) | 自定义模板数组, 生成x行y列都是z的数组 |
| np.eye(x) | 创建一个正方的x*x单位的矩阵, 对角线为1, 其余为0 |
| np.flatten() | 数组降维, 不改变 原值 |
| np.random.rand(x, y, z) | 生成一个一维x随机数或生成x*y的随机数组 |
| np.random.randn(x, y) | 正态分布随机数 |
| np.random.randint(low, high, (shape)) | 整数随机数 |
| np.random.normal(loc, scale, (size)) | 从指定正态分布中抽取样本, loc为概率分布的均匀值, 标准差scale |
| np.random.seed(s) | 给一个随机数字固定 |
| np.randomunifrom(low, high, (size)) | 均匀分布的数组, 有小数 |
| np.random.shuffle(a) | 将数组a的第0轴(最外维度)进行随机排列(洗牌), 改变数组a, 行边列不变 |
| np.random.permutation(a) | 同上, 不改变数组a |
| np.random.choice(a, size=None, replace=False, p=数组a/np.sum(b)) | 从一维数组a中以概率p抽取元素,形成size形状新数组,replace表示是否可以重用元素,默认为False,p为抽取概率,本位置越高,抽取概率越高 |
| np.sum(axis=None) | 求和, axis=0为列, 1为行 |
| np.argsort() | 矩阵每个元素坐标排序 |
| np.sort(axix=None) | 从小打大排序 |
| -np.sort(axis=None) | 从大到小排序 |
| np.sort_values(‘字段’, ascending=False) | 排序,升序排列 |
| np.mean(axis=None) | 平均数 |
| np.average(axis=None,weights=None) | 加权平均,weights加权值,不设为等权重,例子[10, 5, 1],每列分别X10,X5,X1在/(10+5+1) |
| np.var(axis=None) | 方差:各数与平均数之差的平方的平均数 |
| np.std(axis=None) | 标准差:方差平方根 |
| np.min(axis=None) | 最小值 |
| np.argmin(axis=None) | 求数组中最小值的坐标 |
| np.median(axis=None) | 中位数 |
| np.ptp(axis=None) | 元素最大值与最小值的差 |
| np.cumsum() | 累加,cumsum和cumprod之类的方法不聚合,产生一个中间结果组成的数组,默认一维数组,1为按原样 |
| np.cumprod() | 累乘 |
| np.count_nonzero(arr > 0) | 计数非0值个数,布尔值会被强制转换为1和0,可以使用sum()对布尔型数组中的True值计数 |
| np.bools.any() | 测试数组中是否存在一个或多个True |
| np.bools.all() | 数组中所有值是否都是True, 测试有没有空值 |
类型
| np.dtype类型 | 解释 |
|---|---|
| np.bool | 布尔值 |
| np.int | 整型 |
| np.float | 浮点型 |
| np.complex | 复数 |
| np.object | 对象 |
| np.string_ | ASCII字符 |
| np.unicode_ | Unicode所有字符, 字节数平台决定 |

Comments