以示例的方式演示常用包的用法,更详细深入的信息请参考 https://golang.google.cn/pkg/标准库
os
os包提供了操作系统函数的不依赖平台的接口。设计为Unix风格的,错误处理是go风格的;失败的调用会返回错误值而非错误码。- 通常错误值里包含更多信息。
os包的接口规定为在所有操作系统中都是一致的。
打开一个文件并从中读取一些数据。
file, err := os.Open("file.go")
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
如果打开失败,错误字符串是自解释的。open file.go: no such file or directory
文件的信息可以读取进一个[]byte切片。Read和Write方法从切片参数获取其内的字节数。
data := make([]byte, 100)
count, err := file.Read(data)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
fmt.Printf("read %d bytes: %q\n", count, data[:count])
标准的文件信息
type FileInfo interface {
Name() string // base name of the file
Size() int64 // length in bytes for regular files; system-dependent for others
Mode() FileMode // file mode bits
ModTime() time.Time // modification time
IsDir() bool // abbreviation for Mode().IsDir()
Sys() interface{} // underlying data source (can return nil)
}
常用方法
- Stat
func Stat(name string) (fi FileInfo, err error)Stat返回一个描述name指定的文件对象的FileInfo。f, _ := os.Stat(`main.go`) fmt.Println(f.Name(), f.IsDir(), f.ModTime()) - Mkdir
func Mkdir(name string, perm FileMode) errorMkdir使用指定的权限和名称创建一个目录。os.Mkdir(`dir`, 0777)
MkdirAll
func MkdirAll(path string, perm FileMode) errorMkdirAll使用指定的权限和名称创建一个目录,包括任何必要的上级目录,并返回nil,否则返回错误。
权限位perm会应用在每一个被本函数创建的目录上。
如果path指定了一个已经存在的目录,MkdirAll不做任何操作并返回nil。os.MkdirAll(`a/b/c/d`, 0777)
Rename
func Rename(oldpath, newpath string) error
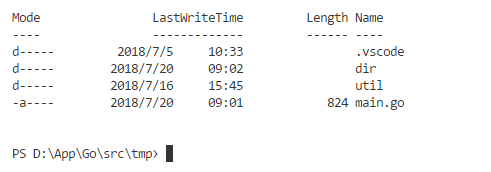
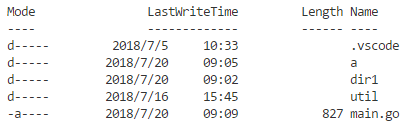
Rename修改一个文件的名字,移动一个文件。可能会有一些个操作系统特定的限制。os.Rename(`dir`, `dir1`)
- Remove
func Remove(name string) error
Remove删除name指定的文件或目录。os.Remove(`dir1`)
- RemoveAll
func RemoveAll(path string) error
RemoveAll删除path指定的文件,或目录及它包含的任何下级对象。它会尝试删除所有东西,除非遇到错误并返回。
如果path指定的对象不存在,RemoveAll会返回nil而不返回错误。os.RemoveAll(`a`)
Create
func Create(name string) (file *File, err error)Create采用模式0666✋创建一个名为name的文件,如果文件已存在会置为空文件。
如果成功,返回的文件对象可用于I/O;对应的文件描述符具有O_RDWR模式。Open
func Open(name string) (file *File, err error)Open打开一个文件用于读取。如果操作成功,返回的文件对象的方法可用于读取数据;对应的文件描述符具有O_RDONLY模式。fout, _ := os.Create(`output.txt`) fin, _ := os.Open(`main.go`) io.Copy(fout, fin)//io包- OpenFile
func OpenFile(name string, flag int, perm FileMode) (file *File, err error)OpenFile是一个更一般性的文件打开函数,大多数调用者都应用Open或Create代替本函数。
它会使用指定的选项(如O_RDONLY等)、指定的模式(如0666等)打开指定名称的文件。
如果操作成功,返回的文件对象可用于I/O。fout, _ := os.Create(`output.txt`) fin, _ := os.OpenFile(`main.go`, os.O_RDWR, 0666) io.Copy(fout, fin) - Readdir
func (f *File) Readdir(n int) (fi []FileInfo, err error)Readdir读取目录f的内容,返回一个有n个成员的[]FileInfo,采用目录顺序。 对本函数的下一次调用会返回上一次调用剩余未读取的内容的信息。
如果n>0,Readdir函数会返回一个最多n个成员的切片。
如果n<=0,Readdir函数返回目录中剩余所有文件对象的FileInfo构成的切片。dir, _ := os.Open(`util`) dirs, _ := dir.Readdir(-1) for idx := range dirs { fmt.Println(dirs[idx].Name()) } - Read
func (f *File) Read(b []byte) (n int, err error)Read方法从f中读取最多len(b)字节数据并写入b。它返回读取的字节数和可能遇到的任何错误。文件终止标志是读取0个字节且返回值err为io.EOF。 - Write
func (f *File) Write(b []byte) (n int, err error)Write向文件中写入len(b)字节数据。它返回写入的字节数和可能遇到的任何错误。如果返回值n!=len(b),本方法会返回一个非nil的错误。 - Close
func (f *File) Close() errorClose关闭文件f,使文件不能用于读写。它返回可能出现的错误。fin, _ := os.Open(`main.go`) fout, _ := os.Create(`output.txt`) //准备容器 buf := make([]byte, 128) for { n, err := fin.Read(buf) if n == 0 || err == io.EOF { break } fout.Write(buf[:n]) } fin.Close() fout.Close() WriteStringfunc (f *File) WriteString(s string) (ret int, err error)WriteString类似Write,但接受一个字符串参数。
fout, _ := os.Create(`output.txt`)
defer fout.Close()
fout.WriteString(`WriteString`)
io && ioutil
eof
var EOF = errors.New("EOF")EOF当无法得到更多输入时,Read方法返回EOF☂️。当函数一切正常的到达输入的结束时,就应返回EOF。Copy
func Copy(dst Writer, src Reader) (written int64, err error)- 将
src的数据拷贝到dst,直到在src上到达EOF或发生错误。返回拷贝的字节数和遇到的第一个错误。 - 对成功的调用,返回值err为nil而
非EOF,因为Copy定义为从src读取直到EOF,它不会将读取到EOF视为应报告的错误。fout, _ := os.Create(`output.txt`) fin, _ := os.OpenFile(`main.go`, os.O_RDWR, 0666) io.Copy(fout, fin)ioutil
- ReadAll
func ReadAll(r io.Reader) ([]byte, error)ReadAll从r读取数据直到EOF或遇到error,返回读取的数据和遇到的错误。
成功的调用返回的err为nil而非EOF。因为本函数定义为读取r直到EOF,它不会将读取返回的EOF视为应报告的错误。
package main
import (
"fmt"
"io/ioutil"
"log"
"strings"
)
func main() {
r := strings.NewReader("Go is a general-purpose language designed with systems programming in mind.")
b, err := ioutil.ReadAll(r)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
fmt.Printf("%s", b)
}
- ReadFile
func ReadFile(filename string) ([]byte, error)ReadFile从filename指定的文件中读取数据并返回文件的内容。成功的调用返回的err为nil而非EOF。因为本函数定义为读取整个文件,它不会将读取返回的EOF视为应报告的错误。
package main
import (
"fmt"
"io/ioutil"
"log"
)
func main() {
content, err := ioutil.ReadFile("testdata/hello")
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
fmt.Printf("File contents: %s", content)
}
- WriteFile
func WriteFile(filename string, data []byte, perm os.FileMode) error
函数向filename指定的文件中写入数据。如果文件不存在将按给出的权限创建文件,否则在写入数据之前清空文件。
package main
import "io/ioutil"
func main() {
ioutil.WriteFile("1.txt", []byte(`string`), 0777)
}
- ReadDir
func ReadDir(dirname string) ([]os.FileInfo, error)
返回dirname指定的目录的目录信息的有序列表。
package main
import (
"fmt"
"io/ioutil"
"log"
)
func main() {
files, err := ioutil.ReadDir(".")
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
for _, file := range files {
fmt.Println(file.Name())
}
}
strings
- Compare
func Compare(a, b string) int
Compare returns an integer comparing two strings lexicographically. The result will be 0 if a==b, -1 if a < b, and +1 if a > b.package main import ( "fmt" "strings" ) func main() { fmt.Println(strings.Compare("a", "b")) fmt.Println(strings.Compare("a", "a")) fmt.Println(strings.Compare("b", "a")) } - Contains
func Contains(s, substr string) bool
Contains reports whether substr is within s.package main import ( "fmt" "strings" ) func main() { fmt.Println(strings.Contains("seafood", "foo")) fmt.Println(strings.Contains("seafood", "bar")) fmt.Println(strings.Contains("seafood", "")) fmt.Println(strings.Contains("", "")) } - Count
func Count(s, substr string) int
Count counts the number of non-overlapping instances of substr in s. If substr is an empty string, Count returns 1 + the number of Unicode code points in s.package main import ( "fmt" "strings" ) func main() { fmt.Println(strings.Count("cheese", "e")) fmt.Println(strings.Count("five", "")) // before & after each rune } - HasPrefix
func HasPrefix(s, prefix string) bool
HasPrefix tests whether the string s begins with prefixpackage main import ( "fmt" "strings" ) func main() { fmt.Println(strings.HasPrefix("Gopher", "Go")) fmt.Println(strings.HasPrefix("Gopher", "C")) fmt.Println(strings.HasPrefix("Gopher", "")) } - HasSuffix
func HasSuffix(s, suffix string) bool
HasSuffix tests whether the string s ends with suffix.package main import ( "fmt" "strings" ) func main() { fmt.Println(strings.HasSuffix("Amigo", "go")) fmt.Println(strings.HasSuffix("Amigo", "O")) fmt.Println(strings.HasSuffix("Amigo", "Ami")) fmt.Println(strings.HasSuffix("Amigo", "")) } - Index
func Index(s, substr string) int
Index returns the index of the first instance of substr in s, or -1 if substr is not present in s.package main import ( "fmt" "strings" ) func main() { fmt.Println(strings.Index("chicken", "ken")) fmt.Println(strings.Index("chicken", "dmr")) } - Join
func Join(a []string, sep string) string
Join concatenates the elements of a to create a single string. The separator string sep is placed between elements in the resulting string.package main import ( "fmt" "strings" ) func main() { s := []string{"foo", "bar", "baz"} fmt.Println(strings.Join(s, ", ")) } - Replace
func Replace(s, old, new string, n int) string
Replace returns a copy of the string s with the first n non-overlapping instances of old replaced by new. If old is empty, it matches at the beginning of the string and after each UTF-8 sequence, yielding up to k+1 replacements for a k-rune string. If n < 0, there is no limit on the number of replacements.package main import ( "fmt" "strings" ) func main() { fmt.Println(strings.Replace("oink oink oink", "k", "ky", 2)) fmt.Println(strings.Replace("oink oink oink", "oink", "moo", -1)) } - Split
func Split(s, sep string) []stringSplit slices s into all substrings separated by sep and returns a slice of the substrings between those separators.package main import ( "fmt" "strings" ) func main() { fmt.Printf("%q\n", strings.Split("a,b,c", ",")) fmt.Printf("%q\n", strings.Split("a man a plan a canal panama", "a ")) fmt.Printf("%q\n", strings.Split(" xyz ", "")) fmt.Printf("%q\n", strings.Split("", "Bernardo O'Higgins")) } ToLower
func ToLower(s string) string
ToLower returns a copy of the string s with all Unicode letters mapped to their lower case.package main import ( "fmt" "strings" ) func main() { fmt.Println(strings.ToLower("Gopher")) }ToUpper
func ToUpper(s string) string
ToUpper returns a copy of the string s with all Unicode letters mapped to their upper case.package main import ( "fmt" "strings" ) func main() { fmt.Println(strings.ToUpper("Gopher")) }Builder
⚡️ A Builder is used to efficiently build a string using Write methods. It minimizes memory copying. The zero value is ready to use. Do not copy a non-zero Builder.type Builder struct { // contains filtered or unexported fields }package main import ( "fmt" "strings" ) func main() { var b strings.Builder for i := 3; i >= 1; i-- { fmt.Fprintf(&b, "%d...", i) } b.WriteString("ignition") fmt.Println(b.String()) }
bytes
bytes包使用方式同strings包bytes包操作对象为[]bytestrings包操作对象为string
直接操作不舒服 正则走一波




Comments